Pop-ups
Pop-up windows which can be used to interrupt the user by asking question or providing information.
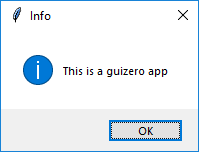
Using pop-ups
Pop-ups can be called from an App or Window object, for example:
app.info("info", "this is a guizero app")
Pop-ups can also be imported individually at the start of your program, for example:
from guizero import info
info("info", "this is a guizero app")
Purpose
These functions pop up a box on the screen that displays a message or asks a question. The functions available are:
warn(title, text)- popup box with a warning iconinfo(title, text)- popup box with an information iconerror(title, text)- popup box with an error iconyesno(title, text)- popup box with yes and no options. PressingYesreturnsTrueand pressingNoreturnsFalse.question(title, text, initial_value=None)- popup box with a question box which can accept a text response. PressingOkreturns value entered into the box is returned and pressingCancelreturnsNone.select_file(title="Select file", folder=".", filetypes=[["All files", "*.*"]], save=False, filename="")- popup file dialog box which asks the user to select a file. By default, an Open button is displayed, settingsavetoTruewill change the button to Save as. The path of the selected file is returned by the function. Afilenameparameter can be supplied which will auto populate the file name field.select_folder(title="Select folder", folder=".")- popup box which asks the user to select a folder. The path of the selected folder is returned by the function.select_color(color=None)- popup box which prompts the user to select a color. Setcolorto an#rrggbbto select a default color when the popup opens. PressingOkreturns the select color as a#rrggbbvalue, pressingCancelreturnsNone.
All pop up boxes use the native display, so they will look different depending on your operating system.
Examples
Warning box
This will pop up a warning box with the title "Uh oh!" and the message "You are almost out of biscuits!".
from guizero import App
app = App(title="Biscuit monitor")
app.warn("Uh oh!", "You are almost out of biscuits!")
app.display()
On Windows, the box looks like this:
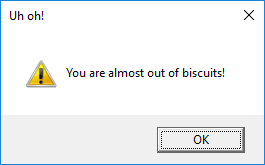
The info and error boxes work in exactly the same way but will display different icons.
Yes/No box
When this function is called it returns a boolean value.
- If
Yeswas pressed, returnTrue - If
Nowas pressed, returnFalse
You can store this value in a variable and test it:
from guizero import App
app = App(title="Snowman")
build_a_snowman = app.yesno("A question...", "Do you want to build a snowman?")
if build_a_snowman == True:
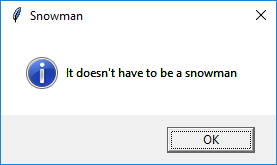
app.info("Snowman", "It doesn't have to be a snowman")
else:
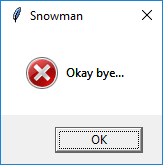
app.error("Snowman", "Okay bye...")
app.display()
This code will first display the yes/no box
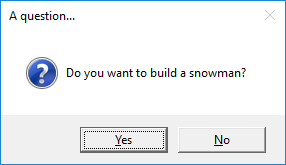
If Yes is pressed, an information box will be displayed:
If No is pressed, an error box will be displayed
Example: Using an alert as a callback
You can also use these functions in a callback (when you have to provide a function for another widget to call). Here is an example with a PushButton which pops up an info box when it is pressed.
from guizero import App, PushButton, info
app = App()
button = PushButton(app, command=app.info, args=["Info", "You pressed the button"])
app.display()
The arguments provided to the PushButton are:
- Where the button should be created (within the
app) - The name of the function to call when pressed (
info) - A list of the arguments to the function you are calling (values for the
titleandmessagearguments for theinfofunction)
Example: Do you really want to close?
You can use a yesno box to check whether someone really wants to exit your app. If they click yes, the app is closed, if not, nothing happens and they can continue with what they were doing.
from guizero import App, Text
# Ask the user if they really want to close the window
def do_this_when_closed():
if app.yesno("Close", "Do you want to quit?"):
app.destroy()
app = App()
title = Text(app, text="blank app")
# When the user tries to close the window, run the function do_this_when_closed()
app.when_closed = do_this_when_closed
app.display()
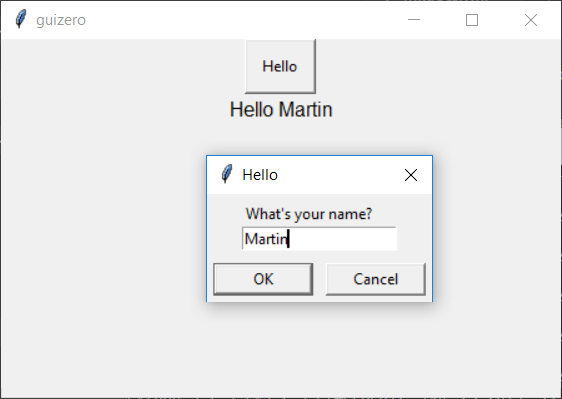
Example: Asking a question
You can use a question pop-up to get information from the user. In this example the user is asked to enter their name when a button is pressed.
from guizero import App, PushButton, Text
def button_pressed():
name = app.question("Hello", "What's your name?")
# If cancel is pressed, None is returned
# so check a name was entered
if name is not None:
hello.value = "Hello " + name
app = App()
button = PushButton(app, command=button_pressed, text="Hello")
hello = Text(app)
app.display()
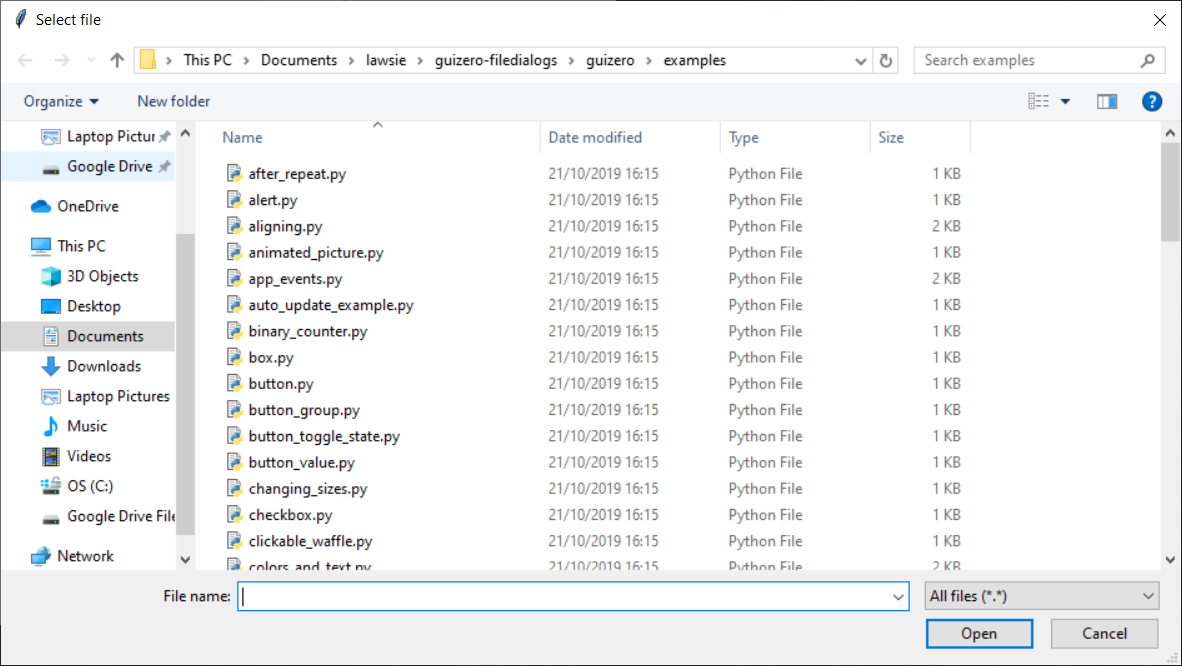
** Example: Get a file name**
Ask the user to select a file using the select_file pop-up.
from guizero import App, PushButton, Text
def get_file():
file_name.value = app.select_file()
app = App()
PushButton(app, command=get_file, text="Get file")
file_name = Text(app)
app.display()
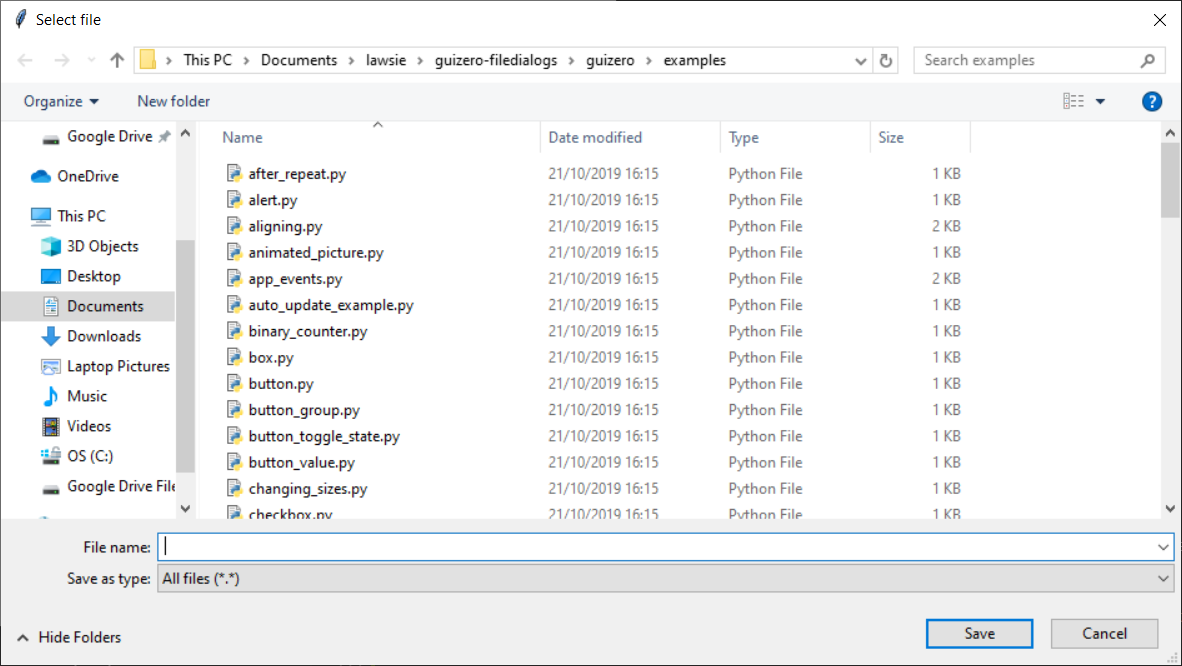
You can change the file type filter by providing a list of type descriptions and extensions as the filetypes parameter e.g.
file_name.value = app.select_file(filetypes=[["All files", "*.*"], ["Text documents", "*.txt"]])
The default is to show an Open button, this can be changed to a Save button by setting the save parameter to True e.g.
file_name.value = app.select_file(save=True)
** Example: Get a folder name**
Select a folder using the select_folder pop-up.
from guizero import App, PushButton, Text
def get_folder():
path.value = app.select_folder()
app = App()
PushButton(app, command=get_folder, text="Get path")
path = Text(app)
app.display()

You can set the initial folder by passing a path to the folder parameter
file_name.value = app.select_file(folder="c:\users\lawsie")